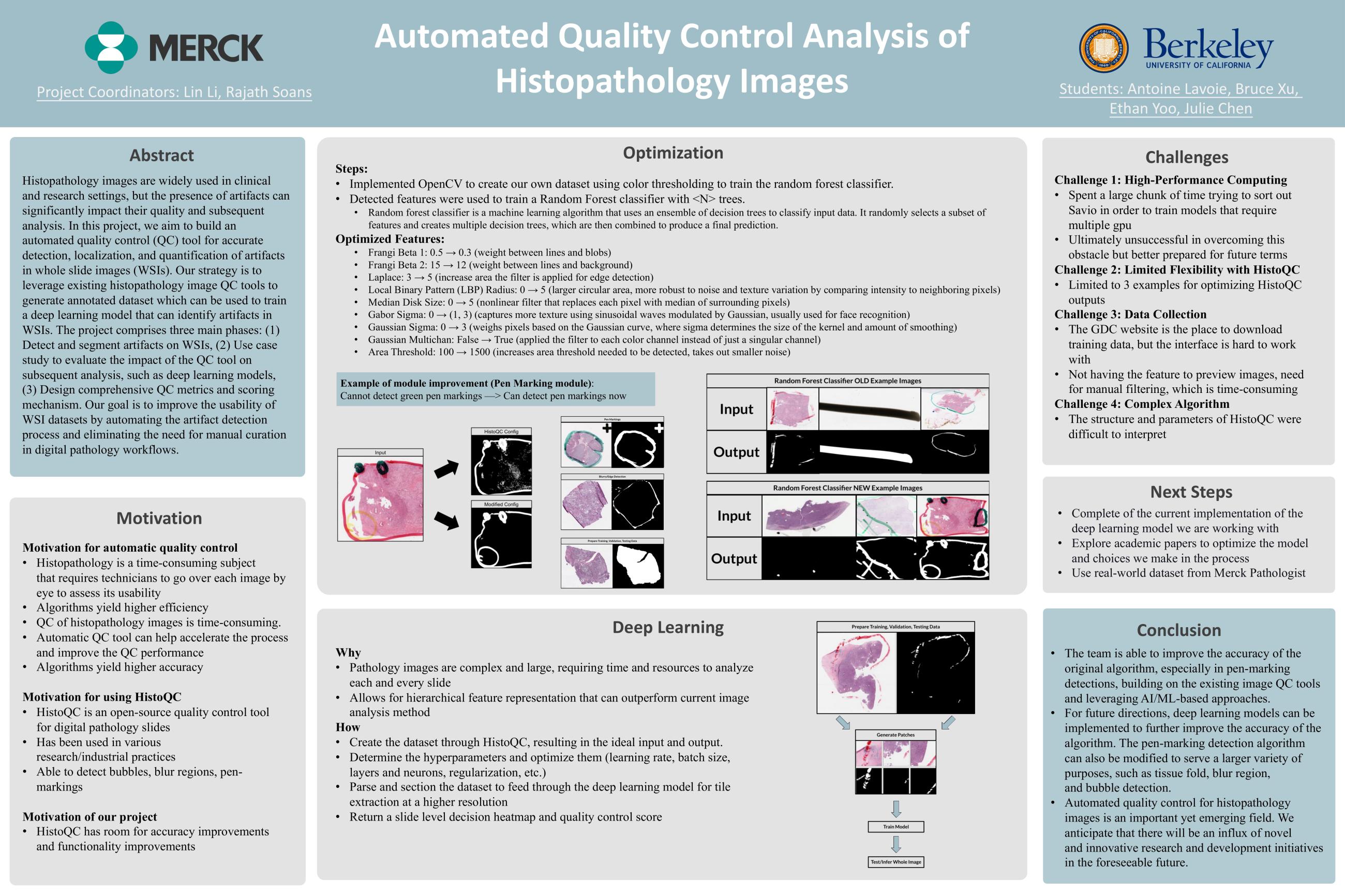
Digitally scanned whole slide image (WSI) have increasingly involved in both clinical and non-clinical disease diagnostic workflow and enabled active research in computational pathology. However, the presence of artifacts on WSI, including tissue tearing, folding, blurring, air bubbles, etc., can significantly affect the downstream workflows and analysis. The regions affected by artifacts should be eliminated before the data can be used in the subsequent analysis. Manual review of the DP scans is laborious, qualitative and subject to intra- and inter-reader variability. So, this study aims to build an automated quality control (QC) tool to accurately localize and quantify the artifacts in the WSI and produce comprehensive QC report to guide the use of the DP scans in the subsequent analysis or provide the feedback to help digital pathology labs in QC and analysis.
This study comprises of three main phases:
(1) Detect and segment the region of artifacts on the WSIs, including tissue tearing, folding, blurring, air bubbles, and pen markers.
(2) Design comprehensive QC matrices and QC score based on the detected artifacts on WSIs.
(3) Use case study: apply this QC tool to evaluate if it can help improve the subsequent analysis performance, e.g., deep learning model.
We are planning to leverage existing histopathology image QC tools while are open to AI/ML based QC approaches based on the team’s skills, time, and availability of computing resource.